
BRIC-Link - Low-Cost IP Audio Codec *Discontinued*

The Comrex BRIC-Link is a low-cost, high-performance solution for audio-to-IP conversion, designed for point-to-point and point-to-multi-point audio connections using IP connectivity.
Based on the core technical aspects of the industry-standard Comrex ACCESS-IP Remote Broadcast product line, BRIC-Link provides an elegant way of moving Linear or Compressed audio with very low delay. BRIC-Link may be used over a range of IP links, is very simple to use and avoids the need to buy features that are not required for this type of application. While BRIC-Link has an entry-level price, it maintains superb audio specifications and hardware reliability, making the system suitable for STL Studio-Transmitter Links and other mission-critical functions.

BRIC-Link has been designed for point-to-point “nailed up” high-quality audio links over a variety of data networks such as ISM band IP radios, T1 carriers, satellite channels, WANs and LANs. The robustness of the BRIC technology (Broadcast Reliable Internet Codec) used in the box allows the system to perform well on the public Internet as well (using AAC compression modes).
As well as its compressed audio codecs, BRIC-Link offers a robust stereo or mono Linear mode that does not compress audio. In addition, unique to real-time audio codecs, BRIC-Link offers FLAC* lossless compression, reducing network throughput by 30-40% with absolutely transparent coding and no tandem coding concerns. For situations where more reduced bandwidth is desired, BRIC-Link offers AAC/HE-AAC modes as standard, allowing superb audio quality at dramatically reduced data rates.

BRIC-Link is a true codec, offering a full-duplex stereo encoder and decoder in each box. Where two-way transmission is not required, the reverse channel may be disabled. The BRIC technology incorporated includes a jitter buffer manager that automatically balances delay and stability, dynamically increasing and decreasing delay based on network performance. For networks where the QoS is known, these parameters may be set so that a consistent level of jitter buffer is maintained.

End-to-end coding delay in Linear modes is less than 10mS and FLAC modes are less than 15mS. AAC modes incorporate around 100mS total end-to-end delay and HE-AAC modes deliver around 200mS with much-reduced data bandwidth. Please be aware that in addition to coding delay, network propagation and jitter buffers add delay to any IP link and these are network dependent. Typical figures for managed connections can be as low as 50-100mS but this can increase to around 200mS and above when using the public internet.

The BRIC-Link II has arrived!
The same robust desktop build but some much anticipated new features and all of the pros from the previous generation rolled into one. BRIC-Link II offers balanced, professional level analog I/O on standard XLR connectors. Alternately, the Left I/O connectors may be switched to AES3 digital audio format. BRIC-Link II can be connected to an IP network through a Gigabit Ethernet jack making this more than just a minor upgrade and a front panel headphone jack perfect for audio monitoring.
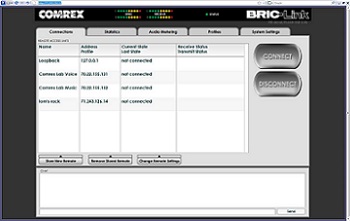
USER INTERFACE
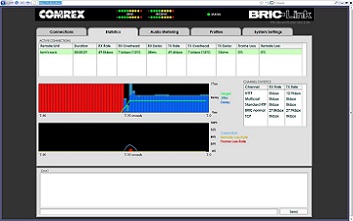
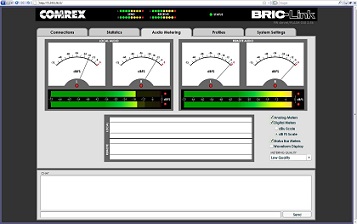
BRIC-Link acts as a web server, delivering an intuitive user interface web page. The page displays connection status and allows the user to configure profiles for various connections, as well as point-and-click connection commands. Extensive network diagnostics are available via the statistics section and audio level meters are available for remote monitoring of levels in and out. Extensive network diagnostics are available via the statistics section and audio level meters are available for remote monitoring of levels in and out.
Initial IP configuration is managed via a Windows-based setup utility to be run on a computer located on the same LAN. The utility also functions as an upgrade utility, allowing flash upgrades from the Comrex website to be applied to the hardware.
BRIC-Link Coding Algorithms:
LINEAR - Uncompressed
BRIC-Link’s linear mode digitizes audio to 16 bit samples. It does not compress the audio further but packetizes a frame of audio samples and transfers them across the network uncorrupted. Analogue audio is sampled at 48 kHz, proving 22 kHz frequency response. If AES/EBU Input/Output is used, BRIC-Link can utilize 44.1 kHz and 32 kHz sampled audio in addition to the standard 48KHz sample rate. As shown in Table 1, this can conserve network bandwidth at the expense of slightly reduced frequency response.
FLAC - Lossless audio compression
BRIC-Link offers the FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Compression) algorithm for those who wish to conserve bandwidth without sacrificing audio quality. Since FLAC is lossless(the exact PCM word applied to the encoder is extracted from the decoder) there are no concerns about artifacts or immunity to further coding in the link. FLAC utilizes a variable output encoder and the data rate will rise and fall based on the ability of the encoder to compress a particular frame of audio. For example, during complete silence FLAC outputs less than 1/10th the data of linear PCM but while encoding full-spectrum, full-scale white noise, the data rate is slightly higher than PCM. However, on average audio, FLAC will typically remove 30-35% of the network data when compared to linear.
FLAC encodes analogue audio at 48 kHz with 16-bit resolution. If AES/EBU In/Out is used, FLAC can utilize 44.1 kHz or 32 kHz sampled audio, further conserving bandwidth. Frequency response and all other specifications are identical to linear with a slightly longer (by 5ms) delay.
AAC - Advanced Audio Encoding
For applications that require reduced bandwidth but excellent audio quality, BRIC-Link can utilize the highly-regarded AAC coding algorithm (licensed by Fraunhofer IIS) to provide near-transparent stereo audio at a data rate of 128 kb/s or lower. Several AAC modes are available that reduce bandwidth and offer a choice of stereo or mono operation.
HE-AAC - High Efficiency Advanced Audio Encoding
To further reduce network bandwidth requirements (for example, for operation on the public Internet) BRIC-Link includes HE-AAC, which combines the coding power of AAC with Spectral Band Replication to reduce the data requirements for high frequencies. HE-AAC is typically deemed to sound nearly as good as AAC at lower network bandwidth. HE-AAC is the standardized version of the algorithm known as AAC-Plus.
Several HE-AAC modes are available that reduce bandwidth and offer a choice of stereo or mono operation. HE-AACv2 is also included, which utilizes parametric stereo encoding resulting in extremely low data rates.
N/ACIP SIP Compatibility
G.711 – µ-law & a-law - are the coding algorithms used by standard digital POTS/PSTN calls and provides normal "telephone quality" 300Hz - 3.4KHz audio. These algorithms are included for compatibility with SIP-style VoIP 'phones and codecs.
G.722 - is the coding algorithms traditionally used by broadcasters used over ISDN for Sport and News commentaries and provide 7KHz low-delay speech and music. This algorithm is also included for compatibility with SIP-style VoIP 'phones and codecs.
Opus – A new dynamic bitrate audio format that is taking Audio and Voice over IP by storm, the BRIC-Links new update to version 3.0 adds support to this format. Opus is a low delay low bit rate and high quality audio codec used by more software and hardware by the minute. This audio format is used by CallMe; our web based subscription codec which can be connected by just about any device with a browser.
BRIC-Link Algorithms
| Algorithm | Audio Bandwidth | Data Bitrate | Coding Delay |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear 48KHz | 22kHz Mono | 768kbit/s | 25mS |
| 22kHz Stereo | 1536kbit/s | 25mS | |
| Linear 44.1KHz* | 20kHz Mono | 705.6kbit/s | 27mS |
| 20kHz Stereo | 1411kbit/s | 27mS | |
| Linear 32KHz* | 15kHz Mono | 512kbit/s | 31mS |
| 15kHz Stereo | 1024kbit/s | 31mS | |
| FLAC 48KHz | 22kHz Mono | 540kbit/s | 30mS |
| 22kHz stereo | 1008kbit/s | 30mS | |
| FLAC 44.1KHz* | 20kHz Mono | 500kbit/s | 32mS |
| 20kHz stereo | 1000kbit/s | 32mS | |
| FLAC 32KHz* | 15kHz Mono | 360kbit/s | 36mS |
| 15kHz stereo | 720kbit/s | 36mS | |
| AAC | 20kHz Mono | 56-64kbit/s | 100mS |
| 20kHz Stereo | 96-256kbit/s | 100mS | |
| HE-AAC | 15-20kHz | 18-48kbit/s | 210mS |
| 20kHz Stereo | 64-96kbit/s | 210mS | |
| 15kHz Stereo v2 | 24-48kbit/s | 250mS | |
| G.711 | 300Hz - 3.4kHz | 64kbit/s | 35ms |
| µ-law & a-law | Mono | ||
| G.722 | 7kHz Mono | 64kbit/s | 35ms |
| OPUS | Mono 48kbps | 48kb/s | 46ms |
| Mono 56kbps | 56kb/s | 46ms | |
| Mono 64kbps | 64kb/s | 46ms | |
| Stereo 64kbps | 64kb/s | 46ms | |
| Stereo 96kbps | 96kb/s | 46ms | |
| Stereo 128kbps | 128kb/s | 46ms | |
| *44.1KHz and 32KHz modes are only supported via AES3 digital audio I/O on both ends of link. *FLAC bandwith is vairiable and based on audio input | |||
ADDITIONAL FEATURES
BRIC-Link provides four end-to-end contact closures that are delivered along with the audio stream in each direction. In addition, the contact closure inputs may be configured to initiate connections. An ancillary data stream is also available via RS232 along with the audio stream. In AAC modes, the system is capable of sending up to 3 one-way encode streams to separate decoders (requiring additional bandwidth) - known as multi-Unicast - and BRIC-Link supports IP Multicast on capable networks.
A new feature is BRIC-Link's streaming capability to a software decoder. BRIC-Link is compatible with Winamp, Windows Media Player, VLC etc and is SHOUTcast™ compatible. MP3 is not currently supported but AAC plug-ins are available for most software codecs.
N/ACIP SIP / EBU-3326 Codec Compatibility
The N/ACIP international committee was set up by the European Broadcast Union to hammer out a common protocol to interconnect codec brands and resulted in EBU-3326, a technical document describing how best to achieve this goal. It defines several encoding algorithms plus the transport layer and incorporates the SIP protocol that determines the handshake that takes place at the start of an IP codec call. ACCESS and BRIC-Link codecs already include SIP compatibility which also has the advantage of making them compatible with with other non-broadcast products such as VoIP hardware, software and mobile phone apps such as the ARC (for Android phones). ACCESS and BRIC-Link do not fully comply with EBU3326 as they do not feature MPEG Layer-II but apart from this, they have been tested to be compatible with several other manufacturers' devices using encoders supported by both products. In general, when connecting between Comrex hardware, it is best to use one of the proprietarty modes which take advantage of other algorithms and special features such as BRUTE (UDP stability enhancement and congestion avoidance).
Two BRIC-Link codecs can be mounted side-by-side using a 1-U rack adapter
| Specifications | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connections: |
|
||||||||||||
| Controls: |
|
||||||||||||
| Front Panel Indicators: |
|
||||||||||||
| Physical Specifications: |
|
||||||||||||





